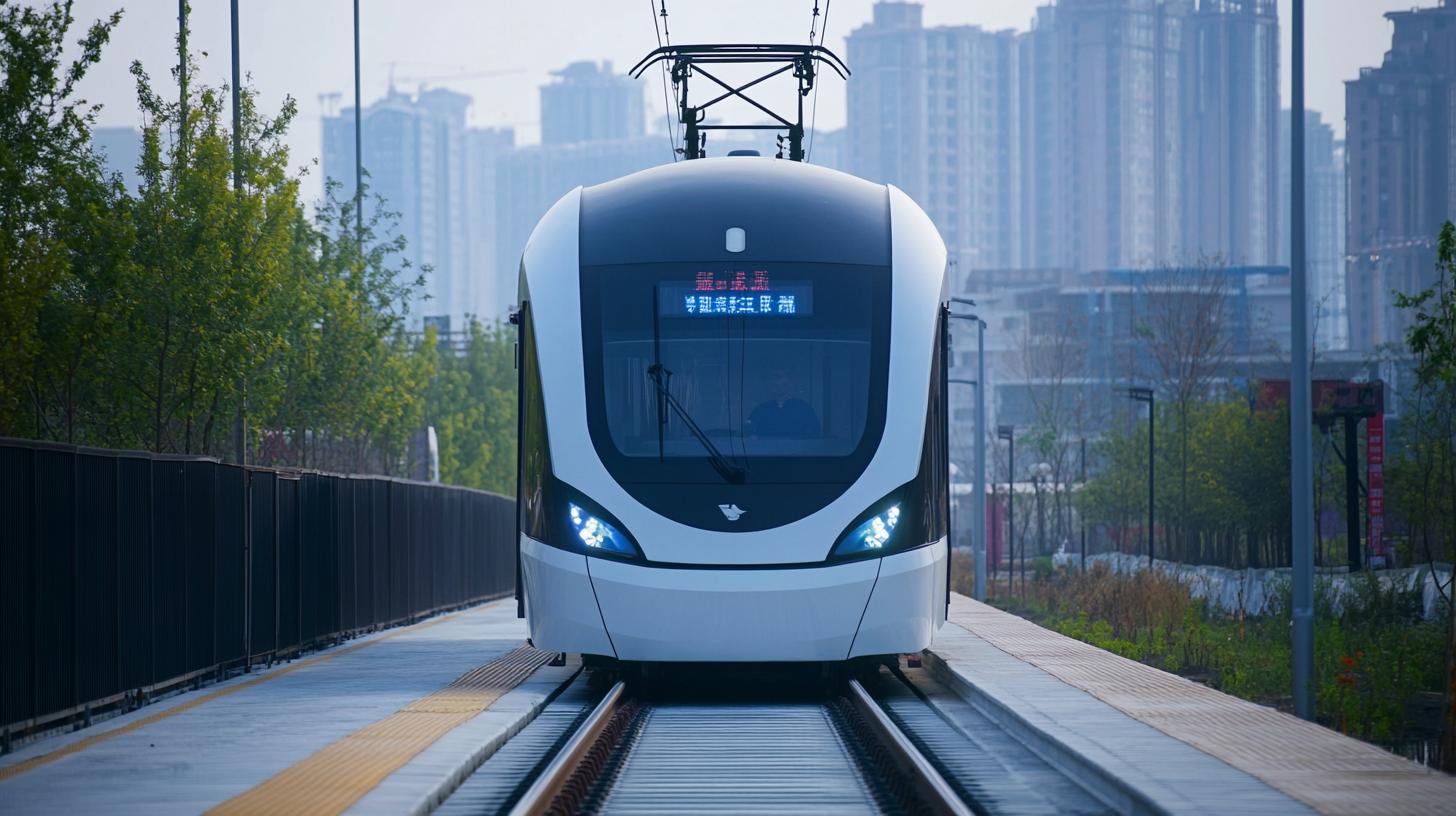
In a groundbreaking move, China’s top electric vehicle battery producers are now utilizing rail transport for domestic deliveries. Faced with escalating costs and increasing demand, battery makers such as Contemporary Amperex Technology Company Limited (CATL) and BYD have begun shipping via specially designed rail containers. This shift marks a potential transformation in logistics, as historically these sensitive products traveled by truck, primarily due to safety concerns.
Supported by the Chinese government, a pilot program has been launched to explore the feasibility and benefits of rail transportation for lithium-ion batteries. CATL’s initial routes connect the cities of Guiyang and Shanghai, as well as Yibin and Shanghai. Meanwhile, BYD has kicked off their rail shipments between Chongqing and Beibu. The long-term vision for these companies includes expanding to international deliveries using the China-Europe Railway Express, a move that could slash shipping times to Europe from 45 days by sea to just 20 days by train.
This development is seen as a significant advancement in battery transportation technology. Rail transport promises not only increased safety for these potentially hazardous goods but also significant reductions in emissions and costs, alongside faster delivery times. As the global push towards sustainable energy solutions gains momentum, China’s innovative approach in reimagining battery logistics could set a new standard worldwide.
The Silent Revolution in Battery Logistics: How Rail Transport is Changing the Game
In an innovative pivot, China’s elite electric vehicle battery producers are pioneering a shift from traditional truck-based logistics to leveraging rail transport for domestic deliveries. This strategic decision, fueled by the rising costs and burgeoning demand, highlights an intriguing transformation in the transportation landscape for these crucial components.
Revolutionizing Battery Logistics: A Move Towards Sustainability
Traditionally, lithium-ion batteries have been transported via trucks, a choice influenced heavily by safety considerations. However, rail transport is emerging as a viable alternative with multiple benefits. It promises increased safety for these sensitive goods and introduces efficiency into the logistics chain with significant reductions in emissions and costs. The ability to deliver faster, especially as global reliance on sustainable energy solutions accelerates, adds another layer of appeal.
One of the standout features of this new approach is the possibility of cutting shipping times dramatically. For instance, when these companies begin utilizing the China-Europe Railway Express, delivery times to Europe could plummet from 45 days by sea to a swift 20 days through overland rail.
Broader Implications: Setting a Global Precedent?
China’s experimental venture into rail transport for lithium-ion batteries, supported by government-backed pilot programs, could well set a global standard. The envisioned future involves expanding this model to international deliveries, a move that will require meticulous planning but offers attractive benefits.
This development is crucial not just for China but also for the global electric vehicle market. Faster logistics mean manufacturers can quickly respond to shifting consumer demands and technological innovations.
Advantages and Disadvantages
So, what are the advantages and potential setbacks of this paradigm shift?
Advantages:
– Safety and Efficiency: Rail transport mitigates the risks associated with handling hazardous materials like lithium-ion batteries.
– Environmental Impact: A reduction in carbon emissions aligns with global environmental goals and combats climate change.
– Cost Effectiveness: Rail can offer a more economical solution compared to road transport over long distances.
– Speed: Cuts delivery time substantially, which is crucial in competitive markets like Europe.
Disadvantages:
– Infrastructure and Initial Costs: Establishing a comprehensive rail network and developing specific containers for battery transport demands substantial initial investment.
– Route and Flexibility Limitation: Unlike trucks, which can access remote locations directly, trains are confined to established tracks and stations.
Unanswered Questions
While the pilot program’s potential seems promising, there remain several questions worth exploring:
– How will other countries respond to China’s advancements in battery logistics?
– What technological innovations will emerge to further secure the safety of battery shipments via rail?
– Could this move lead to a reevaluation of global transportation networks for other sensitive goods?
For more insights into the evolving world of battery manufacturing and transportation, visit CATL and BYD to stay updated on their latest initiatives.
This evolving strategy in battery logistics is not just a milestone in the transport sector but potentially a stepping stone toward a more sustainable and efficient future, reshaping our world one rail line at a time.