Powering the Future of Electric Vehicles in Idaho
Deep in Idaho Falls, the Idaho National Laboratory (INL) is propelling the electric vehicle (EV) revolution with cutting-edge research and development. As electric vehicles surge in popularity, INL’s role in enhancing both battery technology and charging infrastructure is crucial.
Leading Battery Research
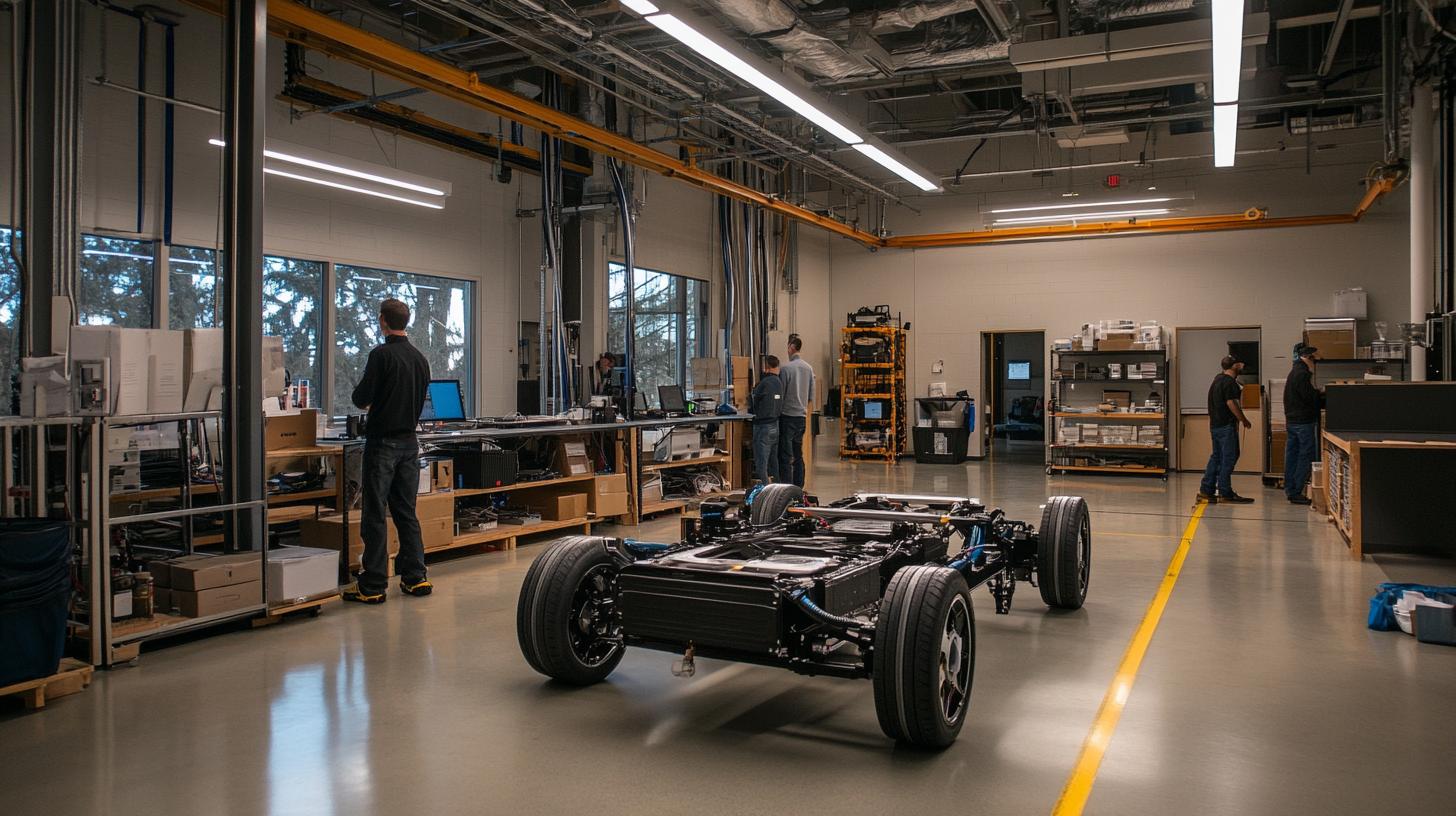
The INL Battery Test Center stands as a cornerstone for advancing EV battery technology. This 17,500-square-foot facility is equipped to test hundreds of batteries simultaneously, allowing researchers to delve deeply into electrochemical processes. Their mission? To create the next generation of batteries that are both more efficient and long-lasting. A leading figure at INL, Pete Barnes, explains that their work focuses on understanding and improving battery performance under various conditions, which can extend the driving range of future electric cars significantly.
Pioneering Charging Solutions
Alongside battery advancements, the INL Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Laboratory (EVIL Lab) is developing technology to support nationwide EV charging networks. These efforts are vital to ensuring convenient and widespread access to charging stations as more drivers switch to electric cars. With efficient charging, individuals can enjoy cost-effective travel, especially in regions like Idaho, where electricity costs are some of the lowest in the country.
Transformative Impact
The influence of INL’s work extends beyond just the local community; it is an integral part of a global shift toward sustainable transportation. As consumer preferences tilt towards electric models, the laboratory’s research is attracting international attention, playing a significant role in the sale of 17 million electric vehicles expected worldwide in 2024. Through their innovative efforts, the Idaho National Laboratory is at the forefront of revolutionizing how we think about travel and energy consumption.
The Silent Revolution: How Idaho’s Electric Vehicle Innovations are Shaping Tomorrow
In the heart of Idaho Falls, the Idaho National Laboratory (INL) is quietly pioneering revolutionary advancements that could reshape the future of transportation and energy consumption worldwide. While most discussions around electric vehicles (EVs) focus on major markets, this laboratory is a testament to the global shift towards sustainable technologies and remains at the forefront of EV innovation.
Beyond Electric Vehicles: The Ripple Effects on Technology
While INL’s efforts in battery research and charging infrastructure are well-documented, there are numerous underreported implications of their work that extend to broader technological horizons. For instance, the laboratory’s deep dive into the electrochemical processes of batteries is not only crucial for EVs but also has significant potential applications in renewable energy storage, a sector rapidly gaining ground as nations work to transition away from fossil fuels.
The challenge of reliable and efficient energy storage has long hindered the expansion of renewable energy sources like wind and solar. By optimizing battery technology, INL’s research could minimize this barrier, facilitating more stable and reliable energy grids that are less dependent on inconsistent fossil fuel supplies. This leap could lead to advancements in smart grid technologies, further integrating renewable sources into our energy mix.
Advantages vs. Disadvantages: A Balanced Perspective
Despite the promising outlook, the path paved by electric vehicles and battery advancements is not without its challenges and controversies.
One of the major benefits of the work being conducted at INL includes the potential reduction in greenhouse gas emissions as electric vehicles replace traditional gasoline-powered ones. This shift promises a cleaner, more sustainable future. Moreover, the possibility of extending battery life and efficiency presents significant cost-saving advantages for consumers and industries alike.
However, this transition is not devoid of drawbacks. The production and disposal of batteries involve resources and processes that are environmentally taxing. The mining of lithium and other critical materials can be harmful to ecosystems, raising ethical and environmental concerns. INL and similar institutions are striving to address these issues by researching recycling methods and sustainable alternatives.
Debate and Curiosity: What’s Next?
The exciting progress at INL invites several questions: How soon can we expect these battery innovations to be mainstream? Will infrastructure keep pace with the rising EV demand? The lab’s ongoing research aims to quickly translate findings into tangible improvements, but widespread adoption relies heavily on economic, political, and social willingness to support necessary infrastructure upgrades and address ethical concerns around resource extraction.
As these developments continue to unfold, the global conversation around EVs and sustainable technology becomes increasingly relevant and urgent. The effects of these innovations are not confined to Idaho or even the United States but resonate around the world, suggesting potential shifts in global energy policies and consumer habits.
Conclusion
The work being done at the INL underscores the transformative power of scientific research and its ability to provide sustainable solutions in an era of climate change and resource scarcity. As the world watches, Idaho stands as an unlikely but vital player in shaping a cleaner and more efficient future.
Suggested related links:
– U.S. Department of Energy
– Vehicle Technologies Office