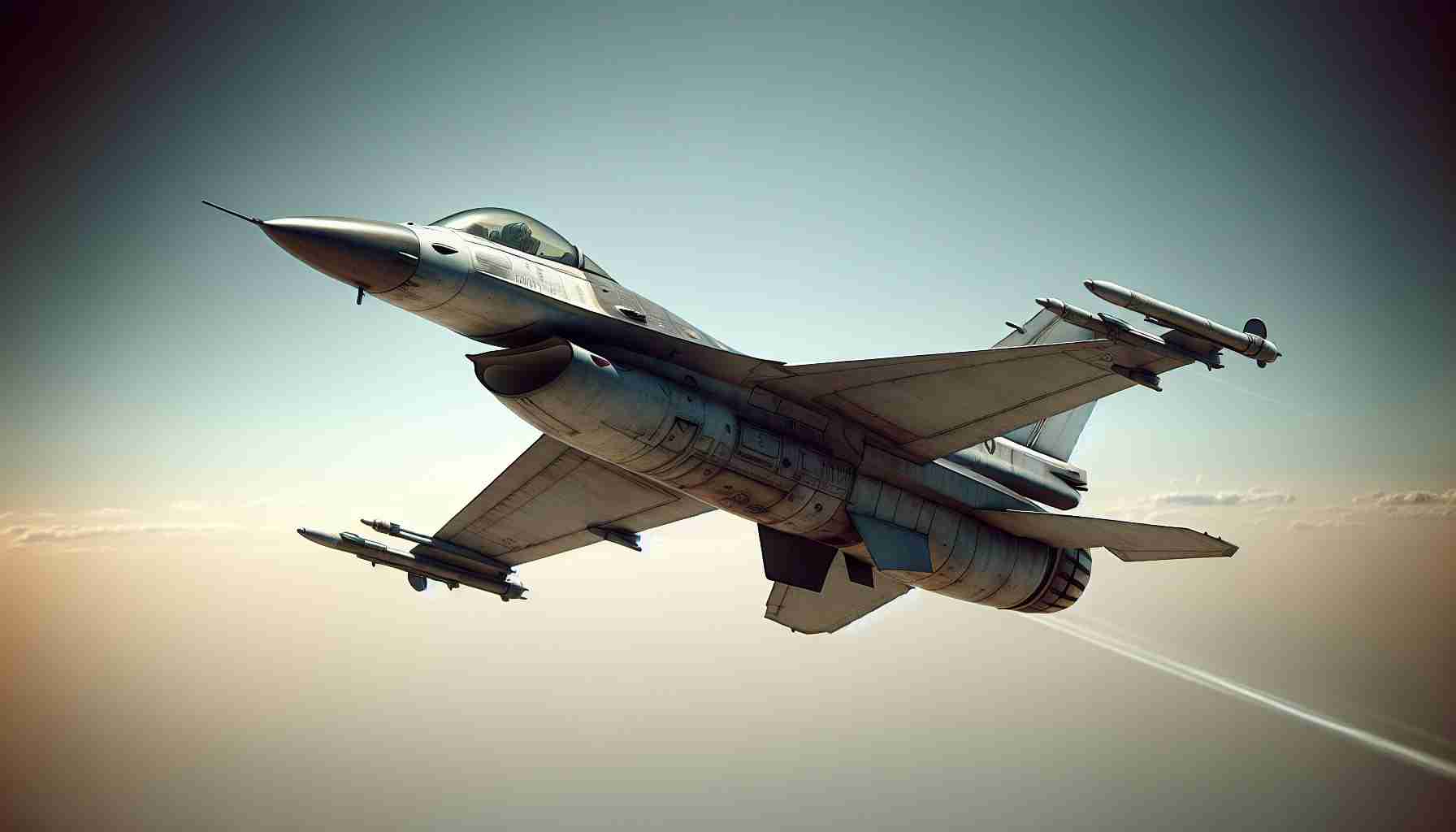
The F-16 Fighting Falcon, a staple of modern air forces, is a testament to enduring military aviation design. But when did this cornerstone of aerial combat first take flight? The story of the F-16 begins in the post-Vietnam War era, where advances in military technology were accelerating, and newer, more versatile aircraft were becoming a priority.
The F-16 was developed by General Dynamics for the United States Air Force and first took to the skies on January 20, 1974. It was officially introduced in 1978, making it a breakthrough in air combat technology. Known for its agility, the F-16 set new standards for what fighter planes could achieve, boasting superior maneuverability and a combat radius that put it ahead of its contemporaries.
Originally conceived as part of the Lightweight Fighter (LWF) program, the F-16 was designed to be relatively inexpensive and easy to maintain. Its affordability and effectiveness quickly led to global adoption, with over 4,600 units built and exported to more than 25 countries.
With continuous upgrades and improvements, the F-16 remains a formidable fighter, illustrating the timelessness of its design and engineering. Its decades-long service history not only underscores its reliability but also serves as a reminder of how visionary designs can remain relevant well beyond their original conception date. Thus, despite being introduced over 40 years ago, the F-16 continues to be a vital component of air defense strategies worldwide.
Why the F-16 Fighter Jet Continues to Make Headlines in Global Defense Strategies
The F-16 Fighting Falcon, though over four decades old, continues to shape global military dynamics today. While much has been discussed about its development and introduction, the modern implications of this aircraft are still unfolding, affecting countless lives worldwide.
What makes the F-16 indispensable? Its continued dominance can be attributed to a blend of cutting-edge technology, adaptability, and cost-effectiveness. As new variants are produced, the F-16 exemplifies the perfect blend of old and new technologies, integrating advanced avionics and weapon systems to meet the changing demands of warfare.
Implications for Communities and Countries
The F-16’s global presence—notably in countries like Israel, Turkey, and South Korea—has strategic implications for how nations assert power and defend sovereignty. It also strengthens international defense partnerships via joint training exercises and technology-sharing agreements.
Controversies and Debate
However, its widespread distribution stirs debate. Critics argue that the proliferation of such powerful military aircraft could increase regional tensions and spark arms races. For example, in some Middle Eastern nations, the F-16 symbolizes both protection and a potential catalyst for escalating conflicts.
Advantages vs. Disadvantages
While it offers excellent agility and a relatively low operational cost, the F-16’s reliance on technology can make it vulnerable to electronic warfare tactics. Moreover, maintaining such an extensive fleet requires significant investment in infrastructure and expertise.
For more insights into global military aircraft developments, visit Lockheed Martin and U.S. Air Force.