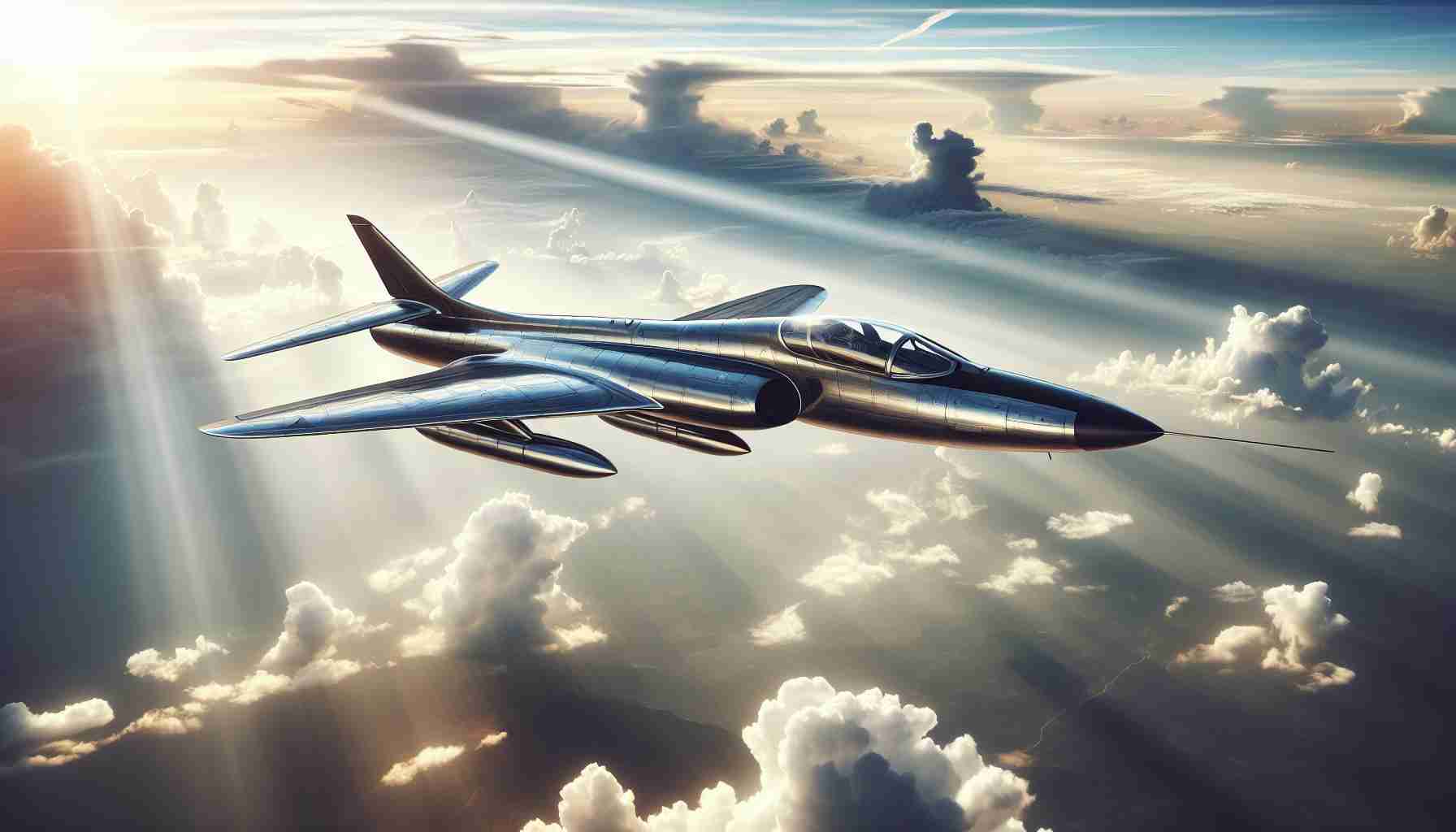
The Dassault Mirage III, a name synonymous with military aviation prowess, stands as a pivotal chapter in the history of jet-powered aircraft. Developed by the French company Dassault Aviation during the 1950s, the Mirage III earned its place as one of the first successful supersonic fighter jets in Western Europe.
Unveiled in 1956, the Mirage III featured a striking delta wing design, which enabled it to excel in high-speed dogfights and climb sharply at high altitudes, characteristics that quickly captured the attention of air forces around the globe. Its robust design and simple yet efficient systems made it an attractive option for many countries seeking to bolster their aerial capabilities during the Cold War era.
Propelled by the powerful SNECMA Atar engine, the Mirage III was capable of reaching speeds up to Mach 2.2, making it one of the fastest jets of its time. Its versatility was soon demonstrated through follow-on versions that adapted to various roles, including interception, ground attack, and reconnaissance missions.
A noteworthy highlight of the Mirage III’s storied career is its performance during the Six-Day War in 1967, where it was utilized effectively by the Israeli Air Force, achieving remarkable success against its adversaries. This cemented the Mirage III’s reputation as a formidable military asset.
To date, the Mirage III’s legacy continues, as it lays the foundation for subsequent aircraft designs while remaining in limited service with several air forces. Its blend of speed, agility, and reliability marks it as a classic example of 20th-century aeronautical achievement that still captures the fascination of aviation enthusiasts worldwide.
Mirage III: A Legacy of Skyward Dominance and Modern Relevance
The Dassault Mirage III, while celebrated for its historic achievements, also brings lesser-known impacts that continue to shape modern aviation strategies and international relations. Beyond its high-speed and agile delta wing design, the Mirage III’s influence extends into contemporary defense ecosystems and political spheres in unexpected ways.
Socio-political Influence: Emerging during the Cold War, the Mirage III became not only a military asset but also a diplomatic tool. Many countries leveraged their acquisition of this supersonic jet to strengthen alliances and assert their strategic independence. How did the Mirage III facilitate geopolitical ties? Nations like Switzerland and Australia, upon integrating the Mirage III into their fleets, bolstered their defense mechanisms without overtly aligning with superpower blocs, illustrating the Mirage III’s subtle diplomatic utility.
Economic Impact: What role did the Mirage III play in local economies? The aircraft’s production led to technological collaborations, benefitting local industries and paving the way for future defense projects. The assembly and maintenance of Mirage IIIs created jobs and infused technological expertise within various countries, notably reinforcing the aerospace sectors of India and Argentina.
Environmental and Technological Innovations: As airforces continue to explore ways to upgrade older airframes, the Mirage III, with its simple yet robust design, sparks discussions on sustainable aviation innovations. What technological advancements are inspired by the Mirage III’s legacy? Its adaptability prompts new considerations for extending the operational life of aircraft through green technologies and more efficient propulsion systems.
Controversial Legacy: Despite its storied past, the Mirage III’s role in conflicts such as the Six-Day War raises ethical questions. Did its success reinforce aggressive military posturing, or was it merely a tool in the geopolitical landscape of its time?
For more insights into aviation history and defense technologies, visit Dassault Aviation and Aerospace Corporation.
The article has been updated: 2024-11-08 07:16
Here are some suggested related links:
1. Military.com – A comprehensive resource for military news, including technology and aircraft developments.
2. U.S. Air Force – The official website of the United States Air Force, featuring information on their aircraft and aviation history.
3. Boeing – The official site of Boeing, the manufacturer of some of the legendary jets that have shaped aerial combat.
4. Aircraft Compare – A platform that provides comparisons and specifications for various military and commercial aircraft.
5. History.com – A rich source of historical information, including articles about military aircraft and significant battles.
6. FlightGlobal – A leading aviation news website that covers all aspects of flight, including military aviation advancements.
7. Lockheed Martin – The official website of Lockheed Martin, known for developing advanced military aircraft that changed the face of aerial combat.
8. Defense.gov – The official website of the U.S. Department of Defense, providing news and updates on military technologies and programs.
9. Airliners.net – A user-generated database of aircraft images and information, including military jets and their operational history.
10. Aviation Week – A leading source for aviation and aerospace industry news, covering military innovations and advancements in aerial combat.
The article has been updated: 2024-11-08 21:14
What are the key features of the legendary jet that changed the landscape of aerial combat?
The legendary jet that redefined aerial combat is often celebrated for several key features. Firstly, its advanced aerodynamics allowed for superior maneuverability and speed, enabling it to outpace adversaries in dogfights. Secondly, it incorporated cutting-edge avionics that improved targeting and situational awareness, giving pilots a tactical advantage. Additionally, its weapon systems were highly versatile, capable of engaging a variety of targets effectively, both in the air and on the ground. Lastly, the jet’s stealth capabilities made it harder for enemy radar systems to detect, significantly enhancing its survivability in combat scenarios. All these elements combined to set a new standard in military aviation, influencing the design and operational strategies of future aerial warfare.