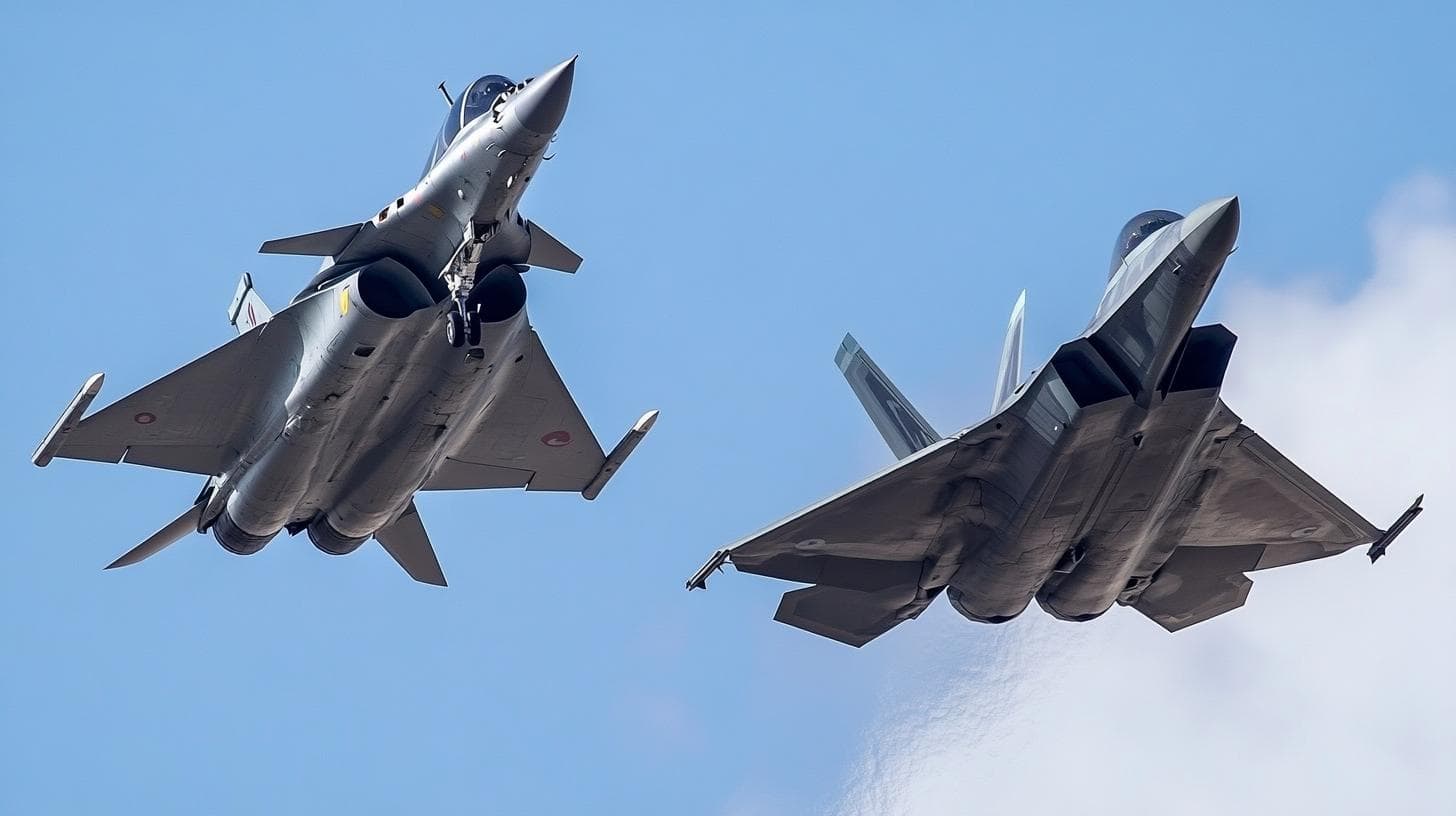
In the realm of modern aerial warfare, mastery of the skies defines military prowess. Air dominance often becomes a decisive factor in conflict, underscoring the necessity for versatile and powerful fighter jets. While many associate this dominance with aircraft like the F-16, F-15, and F-22, the French Dassault Rafale deserves recognition for its remarkable capabilities.
The Rafale: A Multifunctional Powerhouse
The Dassault Rafale emerged from the 1980s as a fourth-generation multi-role fighter aircraft designed to fulfill the wide-ranging requirements of the French Air Force and Navy. Tasked with replacing multiple older aircraft, the Rafale excels in roles from air superiority and strategic attack to intelligence and reconnaissance. Armed to the teeth, it features 14 external hardpoints capable of carrying over 20,000 pounds of weaponry, including diverse missiles and bombs suited for various missions. Its array of powerful armaments positions it as a formidable opponent in any combat scenario.
Technological Prowess and Strategic Flexibility
The Rafale incorporates cutting-edge technology, such as the AESA RBE2 radar for tracking and engaging multiple targets simultaneously and the ingenious “buddy-buddy” refueling capability, which extends its operational range and mission endurance significantly. Powered by twin Snecma M88 engines, the aircraft achieves speeds of up to Mach 1.8 and operates at altitudes reaching 50,000 feet, ensuring its relevance for decades to come.
A Revealing Engagement
In a notable 2009 training exercise, the Rafale showcased its prowess in aerial combat when it “shot down” a U.S. F-22 Raptor in a mock dogfight, an event that marked its technological and strategic strengths. Despite initial denials from the U.S. Air Force, the French released video evidence of the exercise, highlighting the Rafale’s capability when pushed to its limits against stealth fighters. This encounter underscored the Rafale’s exceptional performance and its valuable role in the French military arsenal.
The Impact of Solar Energy Adoption on Global Communities
In recent years, the transition towards renewable energy sources has gained substantial traction worldwide, primarily due to the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. Among the various renewable energy technologies, solar power stands out as a particularly promising and accessible solution. The adoption of solar energy is not just a technological shift; it significantly influences the lives of individuals, communities, and entire nations.
Transforming Lives and Communities
Solar energy adoption can profoundly change the way people live by providing a reliable and sustainable power source. In regions where electricity infrastructure is underdeveloped or unreliable, solar panels offer a decentralized and efficient solution to electrify homes, schools, and hospitals. This is particularly impactful in rural areas of developing countries, where access to electricity can drastically improve quality of life, education, and healthcare.
For instance, in parts of sub-Saharan Africa, community solar projects have enabled residents to power essential appliances, study after dark, and use mobile phones—a lifeline for communication and commerce in remote areas. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), decentralized solar systems in Africa could increase electricity access for over 600 million people.
Economic and Environmental Benefits
Solar energy not only mitigates environmental impact by reducing greenhouse gas emissions but also generates economic opportunities. The solar industry is a robust job creator, with roles ranging from manufacturing and installation to maintenance and research. The U.S. alone has seen a significant rise in solar-related employment, with the industry employing over 230,000 workers as of 2021.
Additionally, widespread solar installation promotes energy independence for countries, lessening reliance on fossil fuel imports and enhancing energy security. Nations like Germany have pioneered large-scale solar initiatives as part of their Energiewende, or energy transition, demonstrating both economic and environmental benefits.
Controversies and Challenges
Despite its many advantages, solar energy adoption is not without its controversies and challenges. One major critique involves the environmental cost of solar panel production, which requires raw materials like silicon, aluminum, and silver, leading to environmental degradation during mining processes. Additionally, the financial burden of initial investment for solar panel systems can be prohibitive for some households and small businesses.
In some regions, solar farms have sparked controversy for their land use, intersecting with issues of agriculture and ecosystem disruption. There are debates about the balance between preserving landscapes and advancing renewable energy goals.
Nevertheless, technological advancements continue to address these challenges. Innovations in solar panel efficiency and recycling processes, coupled with governmental incentives and subsidies, are making solar energy increasingly accessible and sustainable.
For more information on solar energy and its global impact, visit International Energy Agency and U.S. Department of Energy.
In conclusion, the rise of solar energy is reshaping not only how we generate electricity but also how communities function and thrive. As technology advances and adoption grows, solar power will likely play a pivotal role in crafting a sustainable future for generations to come.
The article has been updated. 2024-11-06 08:24
Here are some suggested related links to include in your post about “Aerial Mastery: The Dassault Rafale vs. the F-22 Raptor”:
1. Airforce Technology – A comprehensive resource for military aviation news, featuring articles on various aircraft including the Rafale and F-22.
2. Defense News – Offers the latest updates and analysis on defense-related topics, featuring competitive comparisons of modern fighter jets.
3. Brookings Institution – An independent research organization that provides insights on defense policy, including discussions about advanced military capabilities and air superiority.
4. The Drive – A platform that covers military and civilian aviation, featuring in-depth reviews and comparisons of fighter jets and other aircraft.
5. Janes – A global defense intelligence provider, offering detailed information and comparisons on military aircraft, including the Rafale and F-22.
6. Military.com – A comprehensive resource for military news, featuring articles on various aspects of aircraft performance and military tactics.
7. FlightGlobal – Offers news and analysis on aviation and aerospace, with extensive coverage of military aircraft and their capabilities.
The article has been updated: 2024-11-06 21:18
What are the key differences in operational capabilities between the Dassault Rafale and the F-22 Raptor?
The Dassault Rafale and the F-22 Raptor are both exceptional combat aircraft, but they serve different roles and have distinct operational capabilities.
The F-22 Raptor is primarily designed for air superiority, boasting advanced stealth technology and supercruise capability, allowing it to engage and defeat enemy aircraft with unmatched agility and speed. Its emphasis on air-to-air combat is complemented by advanced avionics and sensor fusion, providing pilots with superior situational awareness.
In contrast, the Dassault Rafale is a multirole fighter, capable of conducting air-to-air combat as well as ground attack missions. While it does incorporate stealth features, it does not match the level of stealth of the F-22. The Rafale is known for its versatility, able to carry a wide range of weapons and execute various missions, including naval operations from aircraft carriers.
Overall, the F-22 excels in air dominance, while the Rafale serves as a flexible multirole platform that can adapt to a broader array of missions.